By establishing a safe, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology improves online privacy and security. By concealing your IP address, it makes your online activity anonymous and shields private information from prying eyes, hackers, and other outside parties. VPNs are frequently used to preserve privacy in an increasingly digital environment, access content that is banned, and browse privately on public Wi-Fi.
What Is a VPN?

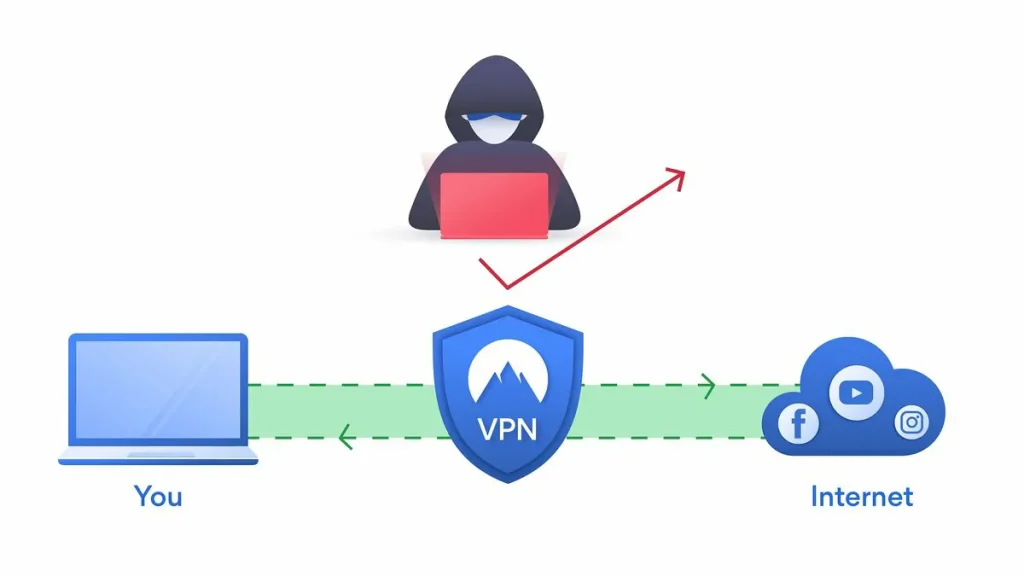
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that allows users to establish a secure and private connection to the internet. It encrypts and redirects your internet traffic through a remote server, concealing your true IP address and location. This keeps your online activity secret and secure from hackers, trackers, and even your internet service provider. VPNs are frequently used to improve online security, gain access to geographically restricted information, and remain anonymous on the internet.
How It Works?
A VPNs establishes a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server managed by the VPNs provider. Here’s how it works, step by step:
- Connection to a VPN Server: When you activate the VPN, your device connects to a server in the location of your choosing.
- Data Encryption: All data transmitted between your device and the server is encrypted to prevent other parties, such as hackers or your internet service provider (ISP), from intercepting or reading it.
- Masking Your IP Address: The VPN server assigns you a new IP address, concealing your true location. Websites and services you visit will display the server’s IP address rather than yours.
- Routing Traffic: Your internet traffic is routed through the VPN server before arriving at its final destination. This provides an additional degree of secrecy and protection because your activities appear to originate from the VPN server.
A VPN protects your online identity, safeguards critical data, and enables you to circumvent geographical restrictions or censorship.
How do I turn on VPN?

Turning on a VPN is dependent on the device and VPN provider you’re using. This is a general guide:
1. Using a VPN App (The Most Common Method)
Download the VPN application: On your device, install the app for the VPN service to which you have subscribed (for example, NordVPN, ExpressVPN, or Surfshark).
Log in: Open the app and log in using your credentials.
Select a server. Select a server region (e.g., United States, United Kingdom, or others) based on your requirements, such as accessing certain content or increasing performance.
Connect: Tap the “Connect” button. The VPN will establish a secure connection and transport your internet traffic through the chosen server.
2. Built-in VPN Features
VPN settings are built-in on many platforms, including Android, iOS, Windows, and macOS.
Windows: Navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > VPN. Create a VPN profile and connect.
macOS: Select System Preferences > Network > VPN. Add and configure VPN settings.
Android: Open Settings > Network & Internet > VPN. Add a VPN and connect.
iOS: Open Settings > General > VPN & Device Management > VPN. Add configuration and connect.
3. Browser-based VPN
Some browsers, such as Opera, include built-in VPN functions that may be enabled in the browser settings.
4. Router-based VPN.
If you want the VPNs to be used automatically by all connected devices, install it directly on your router.
Before utilizing a VPN, make sure you select a reputable provider and double-check your connection.
Is VPN good or bad?
VPNs can be useful or bad depending on how they are used and whose service you choose. Here’s a balanced view:
Positive aspects of VPNs:
Enhanced Privacy: VPNs conceal your IP address and encrypt your internet traffic, making it impossible for hackers, ISPs, and advertising to track your online activity.
Improved Security: Keeps your data safe on public Wi-Fi networks, lowering the danger of hackers.
Access to Restricted Content: Allows you to overcome regional limitations and access websites, streaming services, and content that is not available in your region.
Anonymity: Masks your identity and location, allowing you to remain anonymous.
Avoiding Censorship: Effective in nations with tight internet censorship, allowing access to restricted websites and apps.
Potential drawbacks of VPNs:
Reduced Speed: Data encryption and rerouting can cause a slowdown in your internet connection.
False Security: Not all VPNs are secure; some free or questionable VPN providers may log and sell your information.
Legal and ethical concerns: In some countries, bypassing restrictions with a VPN may be illegal.
Cost: Premium VPNs frequently charge a membership fee.
A VPN can enhance privacy and security when used properly and with a reliable provider. However, it is critical to conduct study and understand the restrictions and legal ramifications in your area.
VPNs can be free or expensive, depending on the supplier. Here’s a breakdown of every option:
Free VPNs have the advantage of being free to use.
Suitable for light and infrequent use.
Simple to setup and utilize.
Cons: Limited functionality, including slower speeds, data limitations, and fewer server locations.
It is possible that there will be insufficient encryption or security.
Some free VPNs collect and sell user data to make money.
Advertisements may appear while using the service.
Advantages of using paid VPNs:
Unlimited bandwidth and higher speeds.
Access to more servers and locations worldwide.
Stronger encryption and more modern security measures.
No-logs policy (with trustworthy providers) provide greater privacy.
Customer support and regular upgrades.
Cons:
It requires a subscription, which normally costs between $2 and $15 each month.
Which should you choose?
Free VPNs are ideal for casual browsing or learning about VPNs. However, they may not be secure enough to do critical operations such as online banking.
Paid VPNs are better suited for everyday use, streaming, gaming, and maintaining privacy and security.
Always conduct thorough research on VPNs providers, especially if you choose a free service, to verify that your data is not compromised.
What is an examples of a VPNs?
Examples of VPNs services are:
Examples of VPNs services are:
- NordVPN is well-known for its excellent security, quick speeds, and extensive network of servers.
- 2. ExpressVPN provides exceptional speed and is user-friendly for streaming and privacy.
- Surfshark – Affordably priced with unlimited simultaneous connections.
- CyberGhost is ideal for novices, with dedicated servers for streaming and gaming.
- ProtonVPN focuses on privacy and provides a dependable free package.
- Windscribe provides both free and premium subscriptions with robust security measures.
- TunnelBear – A user-friendly VPN with a colorful design and a good free plan.
Each VPN offers distinct capabilities designed to meet certain demands, such as streaming, internet privacy, or circumventing censorship.
Conclusion
To summarize, a VPN is an invaluable tool for anybody seeking to improve their online privacy, security, and access to prohibited material. Encrypting your internet traffic and concealing your IP address protects your data from hackers, government spying, and other third parties. A VPN may be a useful tool for surfing on public Wi-Fi, accessing geo-blocked material, or just maintaining your online privacy. However, it is critical to select a reliable VPN provider, as the quality and security of services can vary substantially, particularly with free ones. Finally, a well-chosen VPN may assist assure a more secure and private online experience.




