An Access VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that lets users to securely connect to a private network via the internet, giving them access to resources, services, and data that would otherwise be limited to certain places or devices. It effectively serves as a secure “gateway” to a network, be it a business network, a personal home network, or any other sort of private infrastructure.
Access VPNs are especially beneficial for distant workers who require safe access to corporate systems, individuals who wish to protect their online activity when using public Wi-Fi, and users who want to avoid local content limitations. Access VPNs employ encryption and secure tunneling protocols to keep data secret and safe from hackers, unauthorized users, and monitoring.
This technology is an essential component of current internet security, allowing users to preserve confidentiality, data integrity, and privacy while accessing networks from anywhere in the globe.
What Is a Remote Access VPN?
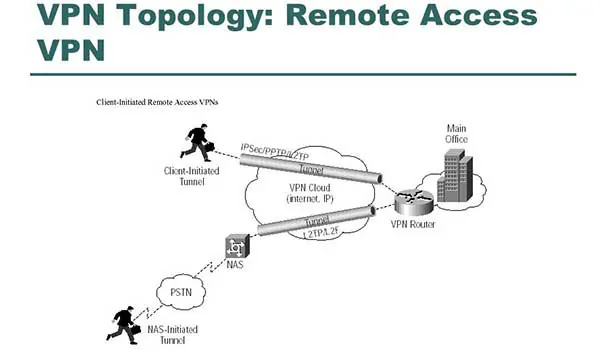
A Remote Access VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a service that allows users to securely connect to a private network, such as a company’s internal network or a home network, from a remote place over the internet. This form of VPN establishes a secure “tunnel” between the user’s device and the private network, encrypting and protecting the data sent and received from unwanted access.
Remote Access VPNs are widely used by enterprises to allow workers to work remotely while preserving secure access to corporate resources such as files, apps, or databases. They are also beneficial for people who wish to securely connect to their home network when traveling or utilizing public Wi-Fi networks.
In short, a Remote Access VPN assures that users may securely access and interact with resources when outside of their trusted network, just as if they were physically there in the office or at home.
What are the uses of remote access?
Uses for Remote Access VPN
A faraway Access VPN has a number of advantages and applications, especially for enterprises and individuals that need to securely access private networks from faraway places. Here are some of the key applications:
Remote Work Access.
Employees may securely access business networks, information, and apps from home, the office, or while traveling. This is especially useful for firms with a scattered staff or those that provide flexible work arrangements.
Secure Collaboration: Employees may collaborate on documents, access internal software, and use team communication tools just as they would in the office.
Accessing Personal Networks.
Home Use: Users may connect to their home network from anywhere, securely connecting to devices like computers, printers, and media servers, as well as retrieving personal information saved at home.
Secure Data Sharing: A Remote Access VPN allows users to securely transmit data between their devices and home network, even when using public Wi-Fi.
Bypassing Geo-restrictions
Accessing Region-Locked Content: Many streaming services, websites, and apps limit access based on your geographic area. Remote Access VPNs allow users to pretend to be accessing the internet from a different place, allowing them to avoid restrictions and access content that is not available in their region.
Secure the internet Browsing over Public Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi Security: Public Wi-Fi networks are frequently insecure, leaving users susceptible to hacking, data theft, and spying. A Remote Access VPN encrypts your internet connection to provide secure surfing and protect personal information from hackers.
Support for mobile devices.
connection via Smartphones and Tablets: Many individuals require network connection when traveling, whether for business or personal reasons. Remote Access VPNs are widely used on mobile devices to provide secure access to private networks from anywhere.
Enhanced privacy and security.
Protection against Tracking: A Remote Access VPN helps avoid third-party tracking of online activity, such as websites, advertising, and hackers, making it a crucial tool for users who respect their privacy.
Encryption: Remote Access VPNs encrypt data so that even if it is intercepted, it remains unreadable and safe.
Accessing Legacy Systems.
Some organizations and people may require access to old systems that require specialized software or configurations that may only be obtained over a secure network. A Remote Access VPN enables remote access to these systems, allowing for continuing use without jeopardizing security.
Support for Remote Customer Service
IT Support: Remote Access VPNs enable IT departments or service providers to securely troubleshoot and resolve issues with remote devices or systems without the requirement for physical presence.
A Remote Access VPN increases personal and company productivity by enabling a secure and private connection to networks from nearly any place, allowing for seamless access to vital resources, sensitive data, and services while improving security and privacy.
Can anyone access my VPN?

No, only authorized people may connect to your VPN. VPNs are intended to safeguard your network and data by allowing only those with the necessary credentials to join. However, there are several important considerations to consider.
1. Strong authentication.
To connect to a VPN, customers normally require a username and password, as well as other security measures such as a two-factor authentication (2FA) code. Unauthorized users cannot connect unless they have these credentials.
2. Encryption
VPNs employ encryption to protect your data while in transit. Even if someone intercepts your connection, they will be unable to view your data since it is encrypted and unreadable.
3. VPN Access Control.
Administrators regulate access to corporate or commercial VPNs by creating user permissions and role-based access restrictions. They can also impose IP-based limitations to limit where connections can originate.
4. Public versus Private VPNs
Private VPN: When you set up a private VPN (for example, at home or for a specialized group), you may limit who has access to it.
Public VPN Providers: If you use a third-party VPN service, the provider may manage access via their infrastructure, but your data is still encrypted, and unauthorized users cannot access it.
5. Security Risks.
While VPNs safeguard your data, weak passwords, obsolete software, or exposed server settings might leave your VPN open to unwanted access. To protect your VPN’s privacy and security, you must perform frequent upgrades, use strong passwords, and follow security best practices.
Can anyone see what you do with a VPN?
When utilizing a VPN, your online behavior is significantly more private compared to browsing without one, but there are still some key aspects to consider regarding who may see what you do:
1. The VPN provider.
What they can see: If your VPN service keeps records, they may be able to observe your online activities, including which websites you visit. However, most good VPN services promote a no-logs policy, which means they do not save any information about your online activity.
They cannot view your encrypted data. Your surfing actions will appear to come from the VPN server’s IP address rather than your own, making it more difficult to track activity back to you.
2. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
What they can’t see: When you use a VPN, your ISP can’t see which websites or services you’re accessing since they only know that you’re connected to a VPN server.
What they can see is that you are using a VPN, but not what you are doing when connected to it.
3. Websites you visit.
What they can’t see: Your true IP address will be hidden by the VPN server’s IP address, so websites will be unable to view it.
What they might see: They can see that you are connecting to their website using a VPN, and if they employ advanced monitoring methods, they may identify patterns in your traffic (such as if you are using a public VPN service), but they will not know your genuine identity.
4. Government agencies.
What they can see: Given the legal authority, various government agencies may request data from VPN companies. This is where the VPN’s logging policy comes into effect. If the supplier does not log data, they have nothing to turn over. However, certain countries may seek to detect VPN usage using modern techniques.
5. Public Wi-Fi networks.
What they can’t see: When using public Wi-Fi networks, your VPN encrypts your internet traffic, shielding it from hackers and other dangerous entities that might try to intercept it.
What they could see: They will see that you are connected to a VPN, but the actual data (websites, messages, etc.) will be encrypted and inaccessible.
Conclusion
While a VPN protects your privacy by masking your browsing activity from ISPs, hackers, and websites, your VPN provider may still be able to view part or all of your actions, depending on their logging methods. If you are really worried about privacy, using a VPN service with a strong no-logs policy and employing extra privacy measures (such as HTTPS websites and secure surfing techniques) will help guarantee that your online behavior stays as secret as possible.



