A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a vital tool for ensuring your online privacy and security. It enables users to browse the internet anonymously, protect their data, and access information from any location in the globe. However, VPNs, like other technologies, have advantages and pitfalls. In this post, we’ll look at the main advantages of utilizing a VPN as well as some potential negatives to think about before choosing if it’s suitable for you.
Top VPN Benefits:
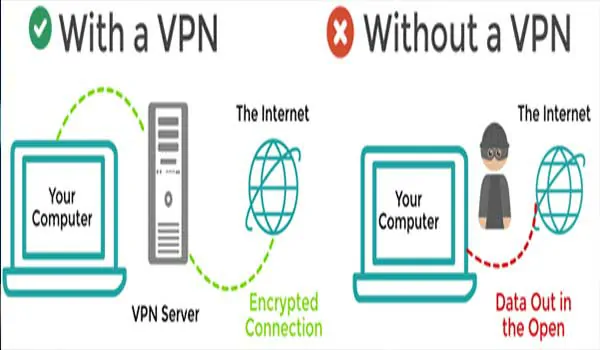
- VPNs provide enhanced privacy by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. This protects your online activity from hackers, websites, and your ISP.
- VPNs improve security by encrypting connections, making it difficult for hackers to capture data on public Wi-Fi networks like cafés or airports.
- Access to Geo-restricted Content
A VPN enables you to circumvent geographic limitations by connecting to servers in various countries. This is great for accessing streaming services such as Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer from anywhere. - Bypass Censorship.
VPNs enable users in countries with tight internet restrictions to access forbidden websites and services, allowing them to browse the internet freely. - Safe online transactions
VPNs protect critical data, such as banking information and passwords, making it far more difficult for fraudsters to steal your information. - Avoid tracking and targeted ads.
A VPN helps limit ad tracking by masking your IP address and preventing tailored advertising from following you throughout the web.
What are the advantages of VPN?
Advantages of Using a VPN: – Increased Privacy
A VPN masks your true IP address, making it impossible for websites, marketers, and even your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to monitor your online activities.
Improved security.
VPNs encrypt your internet connection to safeguard sensitive data such as passwords, credit card information, and personal information from hackers, particularly on public Wi-Fi networks.
Access to Geoblocked Content
A VPN bypasses geographic limitations by connecting to servers in multiple countries, allowing you to access material such as streaming services, websites, and applications that are not accessible in your location.
Bypass Internet Censorship.
In areas with tight internet restrictions, VPNs allow users to access restricted websites and services, protecting information freedom.
Secure online transactions
A VPN encrypts your data, creating a secure environment for online banking, shopping, and other important operations.
Prevent bandwidth throttling.
Some ISPs reduce your internet speed for specific activities such as streaming or gaming. A VPN masks your behavior, which helps you escape throttling.
Anonymous browsing.
VPNs allow you to access the internet anonymously, keeping your identity and location secret.
Remote Work and Safe Data Access
VPNs are commonly used in commercial settings to give employees secure access to company resources from anywhere.
Avoid price discrimination.
Some websites display varying rates for services or items depending on your region. Using a VPN might help you get better discounts.
A VPN is a multipurpose tool that provides privacy, security, and convenience, making it useful for both personal and business purposes.
What is using a VPN good for?

Using a VPN serves various reasons, including increased security, privacy, and access to internet resources. VPNs are widely used for the following purposes:
1. Online Privacy.
A VPN masks your IP address, making it more difficult for websites, advertising, and even your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to trace your online activity.
2. Data Security.
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, protecting sensitive information (e.g., passwords, bank information), particularly while utilizing public Wi-Fi.
3. Accessing Geo-Restricted Content
A VPN connects to servers in other countries, allowing you to bypass geographical restrictions and access streaming platforms, websites, or applications not accessible in your location.
4. Avoiding Censorship.
VPNs offer access to forbidden websites, applications, and services in places where the internet is restricted, providing open access to information.
5. Secure remote work
Businesses frequently use VPNs to allow employees to securely access business resources and sensitive data while working remotely.
6. Gaming Benefits
A VPN can minimize latency, guard against DDoS attacks, and allow players to access games or servers that are blocked by area.
7. Safer Online Transactions
A VPN safeguards online banking, shopping, and other critical activities, shielding you from cyber attacks.
8. Avoiding Price Discrimination.
VPNs can help you save money on flights, hotel reservations, and other services by altering your virtual location.
9. Avoid ISP Throttling
A VPN can assist prevent bandwidth limiting by disguising your activities from your ISP, resulting in better streaming and gaming experiences.
In summary, a VPN benefits anybody who values privacy, security, and unfettered internet access.
Is a VPN really necessary?
 A VPN is required if you value privacy, utilize public Wi-Fi, access geo-restricted material, or require secure remote work. It secures your data, conceals your internet behavior, and circumvents restrictions. However, if you merely surf casually on a secure home network and do not want limited content, it may be unnecessary. A VPN is an excellent alternative for individuals who are concerned about security or who are subject to limitations.
A VPN is required if you value privacy, utilize public Wi-Fi, access geo-restricted material, or require secure remote work. It secures your data, conceals your internet behavior, and circumvents restrictions. However, if you merely surf casually on a secure home network and do not want limited content, it may be unnecessary. A VPN is an excellent alternative for individuals who are concerned about security or who are subject to limitations.
Yes, a VPN can utilize somewhat more bandwidth than a standard connection. This is due to the encryption procedure, which increases the burden on your data. Here’s how:
How VPNs Increase Data Usage:
- Encryption Overhead:
VPNs encrypt your data, adding additional information to keep it safe, which can boost data use by 5-15%.
- Protocol Differences:
The type of VPN protocol you employ (e.g., OpenVPN, WireGuard) influences data overhead. Certain protocols are more efficient than others.
- Routing across servers:
VPN traffic is routed through a distant server, which may add some more data owing to server processing.
Impact on Data Plans:
If you have a restricted data plan, even a small increase might mount up, especially while streaming or gaming. However, the increased security and privacy frequently outweighs the little increase in data use.
Choose efficient protocols such as WireGuard to reduce data impact, and restrict bandwidth-intensive activities.
Conclusion
To summarize, while a VPN marginally increases data use owing to encryption and routing operations, the increase is negligible when compared to the tremendous benefits it brings. Enhanced security, privacy, and access to restricted information frequently exceed any little impact on data. If you have a restricted data plan, you may optimize your consumption by using efficient VPN protocols and carefully controlling high-bandwidth activities. Overall, a VPN remains an important tool for ensuring secure and unfettered internet access.



